Scheduling 의 문제
스프링에서 제공하는 @Scheduled 는 기본적으로 단일스레드로 모든 스케줄링을 순차적으로 관리하게 됩니다. 때문에 스케줄링이 2개 이상이라면 의도했던 것과 다르게 동작할 수 있습니다. 우선 다음과 같은 코드가 있다고 가정하겠습니다.
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class TestScheduler {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000)
public void test1() {
try {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String threadName = currentThread.getName();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("Thread Name : {}, Method Name : {}, time : {}", threadName, methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000)
public void test2() {
try {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String threadName = currentThread.getName();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("Thread Name : {}, Method Name : {}, time : {}", threadName, methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
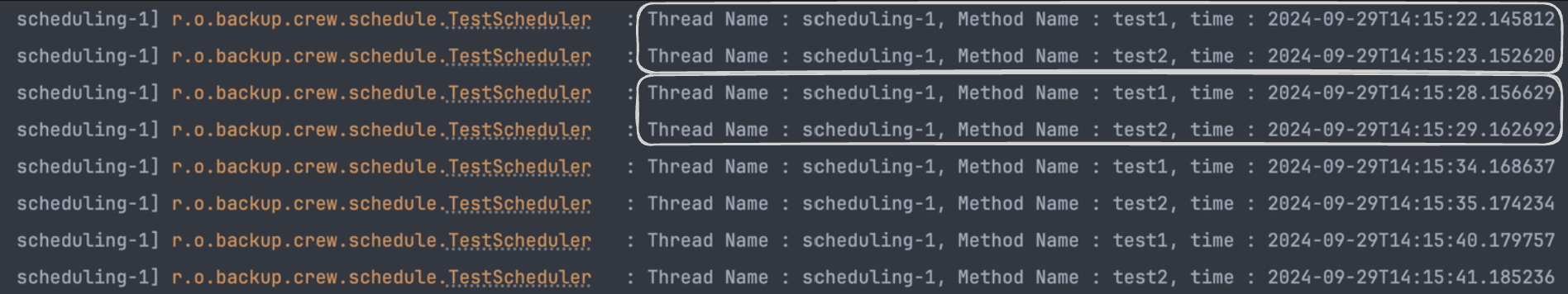
}기대했던것은 test1 메서드는 5초에 한번씩 그리고 test2 메서드는 1초에 한번씩 로그에 찍히는 것입니다. 하지만 아래 로그를 보면 test1, test2 주기가 모두 6초인 것을 볼 수 있다. 이는 스프링의 @Scheduled가 별도의 설정이 없으면 단일 스레드에서 동작한다는 것을 보여주는 예시입니다.
해결방법
따라서 Scheduler 를 만들고 적절한 Thread 개수를 설정하여 Multi Thread 환경을 만든 다음, 스케줄링이 해당 Scheduler 를 사용하게끔 만들어줘야 스케줄링에서 사용하는 스레드들끼리의 간섭을 막아줄 수 있다. 해결방법으로는 SchedulingConfigurer, TaskScheduler, @Async 가 있다.
SchedulingConfigurer
Scheduler 를 설정하는 첫번째 방법은 SchedulingConfigurer 를 구현하여 직접 스케줄러를 등록하는 것입니다. 이를 구현하면, 스케줄러가 사용하는 ThreadPool 의 크기를 조정하거나 Thread 의 이름을 변경하는 등의 동작을 설정할 수 있습니다. SchedulingConfigurer 를 통해 등록된 스케줄러는 기본적으로 모든 스케줄링 메서드에서 사용되게 됩니다.
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class TestScheduler {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000)
public void test1() {
try {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String threadName = currentThread.getName();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("Thread Name : {}, Method Name : {}, time : {}", threadName, methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000)
public void test2() {
try {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String threadName = currentThread.getName();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("Thread Name : {}, Method Name : {}, time : {}", threadName, methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
@Configuration
static class TestTaskConfigurer implements SchedulingConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureTasks(ScheduledTaskRegistrar taskRegistrar) {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolTaskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setPoolSize(2);
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setThreadNamePrefix("sch-");
threadPoolTaskScheduler.initialize();
taskRegistrar.setTaskScheduler(threadPoolTaskScheduler);
}
}
}아래 결과를 보면 task1 의 주기가 5 초, task2 의 주기가 1초. 즉, 스케줄링에서 사용되는 Thread 들끼리의 간섭없이 의도한대로 잘 동작하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. sch- 뒤에있는 숫자가 Thread Pool 설정에서 설정한 N 번째 스레드라는 것을 의미합니다.

TaskScheduler
Scheduler 를 설정하는 두번째 방법은 TaskScheduler 타입의 Bean 을 등록하는 것입니다. 앞서 살펴본 SchedulingConfigurer 와 마찬가지로 ThreadPool 의 크기를 조정하거나 Thread 의 이름을 변경하는 등의 동작을 설정할 수 있습니다. TaskScheduler 타입의 Bean 이 등록되면, 모든 스케줄링 메서드가 등록된 TaskScheduler을 사용하게끔 동작합니다. 물론 직접 스케줄링 메서드마다 스케줄러를 등록해줄 수도 있습니다.
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class TestScheduler {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000)
public void test1() {
try {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String threadName = currentThread.getName();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("Thread Name : {}, Method Name : {}, time : {}", threadName, methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000)
public void test2() {
try {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String threadName = currentThread.getName();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("Thread Name : {}, Method Name : {}, time : {}", threadName, methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
@Bean(name = "testTasks")
public TaskScheduler configureTasks() {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolTaskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setPoolSize(2);
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setThreadNamePrefix("test-sch-");
threadPoolTaskScheduler.initialize();
return threadPoolTaskScheduler;
}
}마찬가지로 의도한대로 동작하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.

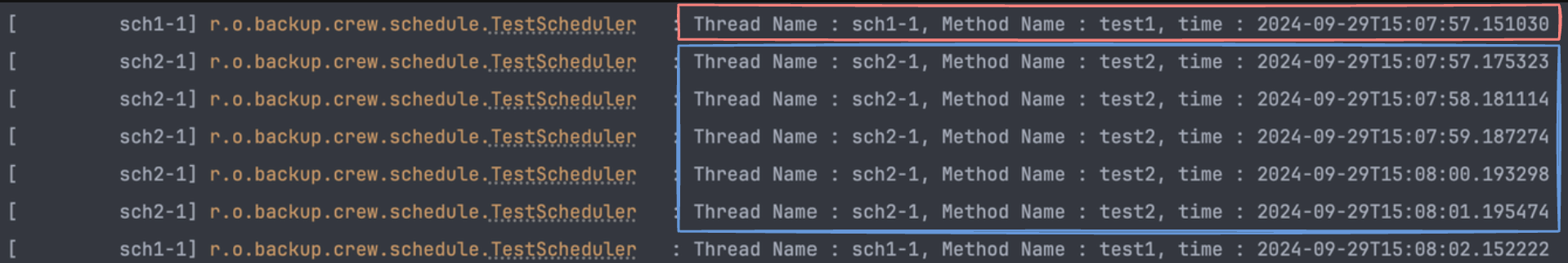
물론 스케줄링 메서드마다 사용할 스케줄러를 지정해줄 수도 있습니다. 아래 코드를 보면 scheduler 라는 속성에 사용할 TaskScheduler 의 이름을 설정해준것을 볼 수 있습니다. 참고로 스케줄러의 이름은 등록한 Bean 이름입니다.
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class TestScheduler {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000, scheduler = "testTask")
public void test1() {
try {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String threadName = currentThread.getName();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("Thread Name : {}, Method Name : {}, time : {}", threadName, methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000, scheduler = "testTask2")
public void test2() {
try {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String threadName = currentThread.getName();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("Thread Name : {}, Method Name : {}, time : {}", threadName, methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
@Bean(name = "testTask")
public TaskScheduler configureTasks() {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolTaskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setPoolSize(1);
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setThreadNamePrefix("sch1-");
threadPoolTaskScheduler.initialize();
return threadPoolTaskScheduler;
}
@Bean(name = "testTask2")
public TaskScheduler configureTasks2() {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolTaskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setPoolSize(1);
threadPoolTaskScheduler.setThreadNamePrefix("sch2-");
threadPoolTaskScheduler.initialize();
return threadPoolTaskScheduler;
}
}마찬가지로 정상적으로 동작하는것을 볼 수 있습니다.
또다른 해결방법으로는 @Async 를 사용하여 작업을 비동기처리시키는 것입니다. 해당 부분에 대해서는 Caller 가 비동기 작업 중 발생한 예외를 받을 수 없다는 것 정도밖에 모르기 때문에, 나중에 알아보도록 하겠습니다.