Scheduling
스케줄링(Scheduling)은 특정 작업이나 프로세스를 정해진 시간에 실행하거나 일정한 주기로 반복해서 실행하는 것을 의미합니다. 컴퓨터 시스템에서 스케줄링은 CPU와 같은 자원을 효율적으로 관리하고, 애플리케이션에서는 주기적인 작업을 자동으로 처리하는 데 사용됩니다. 물론 자바의 진영의 스프링에서는 @Scheduled 애노테이션을 통해 스케줄링을 쉽게 구현할 수 있습니다.
@Scheduling 설정
@Scheduling 을 사용해주기 위해서는 Bean Scan 범위 안에서 @EnableScheduling 를 설정해주어야 합니다.
@EnableScheduling
@Configuration
public class ScheduleConfig {
}@Scheduling 속성
fixedRate
@Scheduling 메서드를 작업의 실행 시점부터 일정 시간동안 반복해서 실행합니다. 기본 시간 단위는 밀리초이지만, timeUnit 속성으로 다른 시간 단위를 설정할 수 있습니다. 정확한 프록세스는 다음과 같습니다.
Started ~~Application in 2.588 seconds (process running for 4.066)- 작업 실행
- 3초 대기
- 작업 실행
- …반복…
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class TestScheduler {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 3, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
public void fixedRate() {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
log.info("Method {} Invoked, Date : {}", methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
fixedDelay
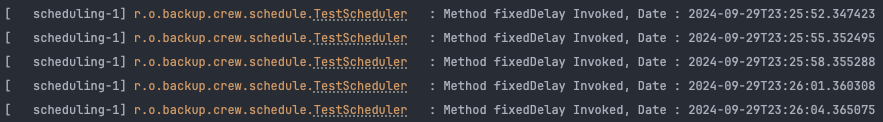
@Scheduling 메서드의 이전 작업이 끝난 시점과 다음에 시작할 작업 사이에 지정한 시간만큼 간격을 두어 작업을 반복합니니다. 마찬가지로 기본 시간 단위는 밀리초이지만 timeUnit 속성으로 다른 시간 단위를 설정할 수 있습니다.
fixedRate 는 작업의 시작시점(호출시점) 부터 시간을 세고, fixedDelay 는 작업이 끝난 시점부터 시간을 셉니다.
앞서 살펴본 fixedRate 와 역할은 동일하지만, fixedDelay 방식은 SimpleAsyncTaskScheduler 와 함께 단일 스케줄러 스레드에서 동작합니다. 정확한 프록세스는 다음과 같습니다.
Started ~~Application in 2.593 seconds (process running for 3.99)- 작업 실행 (마지막 호출)
- 3초 대기
- 작업 실행 (다음 호출)
- …반복…
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class TestScheduler {
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 3, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
public void fixedDelay() {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
log.info("Method {} Invoked, Date : {}", methodName, LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
initialDelay
@Scheduling 메서드의 첫 작업을 실행하기까지 지연시간을 의미합니다. 마찬가지로 기본 시간 단위는 밀리초이지만 timeUnit 속성으로 다른 시간 단위를 설정할 수 있습니다. 정확한 프로세스는 다음과 같습니다.
Started ~~Application in 2.593 seconds (process running for 3.99)- 10 초 (initialDelay) 만큼 대기
- 작업 실행 (마지막 호출)
- 3초 대기 (fixedRate)
- 작업 실행 (다음 호출)
- …반복…
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class TestScheduler {
private final AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Scheduled(initialDelay = 10, fixedRate = 3, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
public void initialDelay() {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
log.info("Method {} Invoked {}th, Date : {}", methodName, atomicInteger.incrementAndGet(), LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
cron
작업 반복을 위한 Cron Expression 을 적어주면 됩니다. 리눅스 crontab 에서 사용되는 Cron Expression 은 5개의 필드로 이루어져 있지만, @Scheduled 에서 사용되는 Cron Expression 은 6개의 필드로 이루어져 있습니다.
리눅스 Crontab
* * * * *
┬ ┬ ┬ ┬ ┬
│ │ │ │ └─ 요일 (0 - 7) (0: 일요일, 1: 월요일, ..., 6: 토요일, 7: 일요일)
│ │ │ └───── 월 (1 - 12)
│ │ └───────── 일 (1 - 31)
│ └───────────── 시간 (0 - 23)
└───────────────── 분 (0 - 59)@Scheduled cron
* * * * * *
┬ ┬ ┬ ┬ ┬ ┬
│ │ │ │ │ └─ 요일 (0 - 7) (0: 일요일, 1: 월요일, ..., 7: 일요일)
│ │ │ │ └───── 월 (1 - 12)
│ │ │ └───────── 일 (1 - 31)
│ │ └───────────── 시간 (0 - 23)
│ └─────────────── 분 (0 - 59)
└─────────────────── 초 (0 - 59) ← 리눅스와의 차이점코드는 매우 간단합니다. 작업을 수행할 주기를 Cron Expression 에 맞게 작성해주면 됩니다. 아래 코드는 5초마다 로그를 찍는 작업을 나타낸 것입니다.
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class TestScheduler {
private final AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
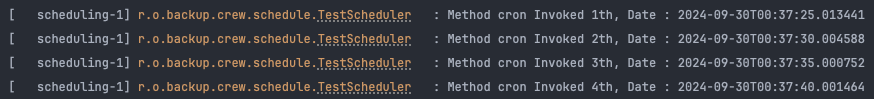
@Scheduled(cron = "*/5 * * * * *")
public void cron() {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
log.info("Method {} Invoked {}th, Date : {}", methodName, atomicInteger.incrementAndGet(), LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
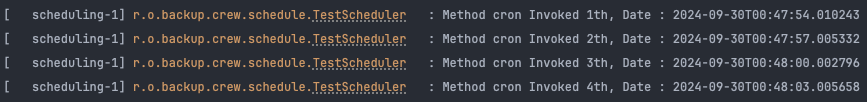
추가적으로 @Scheduled 의 속성들 중 String 값을 갖는 속성들은 스프링 SpEL(SPring Expression Language) 을 사용하여 cron 과 같은 설정을 외부로 분리하여 유연하게 관리할 수 있습니다. 아래 예시는 application.yml 혹은 properties 로부터 schedule.cron.expression 설정을 가져와 cron 값으로 사용할건데, 만약 설정이 되어있지 않다면 Default 로 */3 * * * * * 값을 사용할 것이라는 의미입니다.
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class TestScheduler {
private final AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Scheduled(cron = "${schedule.cron.expression:*/3 * * * * *}")
public void cron() {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String methodName = currentThread.getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
log.info("Method {} Invoked {}th, Date : {}", methodName, atomicInteger.incrementAndGet(), LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
Cron 에 대한 더 자세한 내용은 @Scheduled 어노테이션 Docs 를 보면 됩니다.
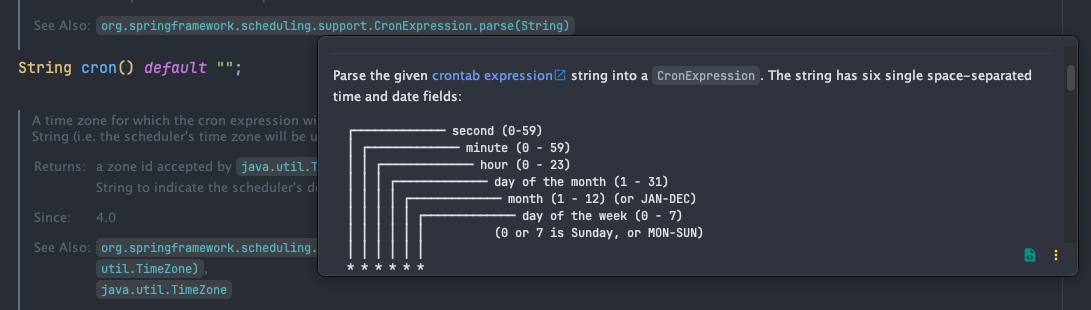
scheduler
@Scheduled 메서드가 사용할 스케줄러를 지정할 수 있습니다. scheduler 의 이름은 TaskScheduler 타입의 Bean 이름을 적어주면 됩니다.
TaskScheduler Bean 이 없거나, SchedulingConfigurer 로 직접 스케줄러를 설정해주지 않으면, Main Thread 는 별도의 Thread 를 만들어 Single Thread 환경에서 모든 스케줄링을 관리하게 됩니다. 아래 사진의 scheduling-1 가 Main Thread 가 스케줄링을 위해 만든 별도의 Thread 입니다. 관련 내용은 다음 포스팅 에서 보실 수 있습니다.
